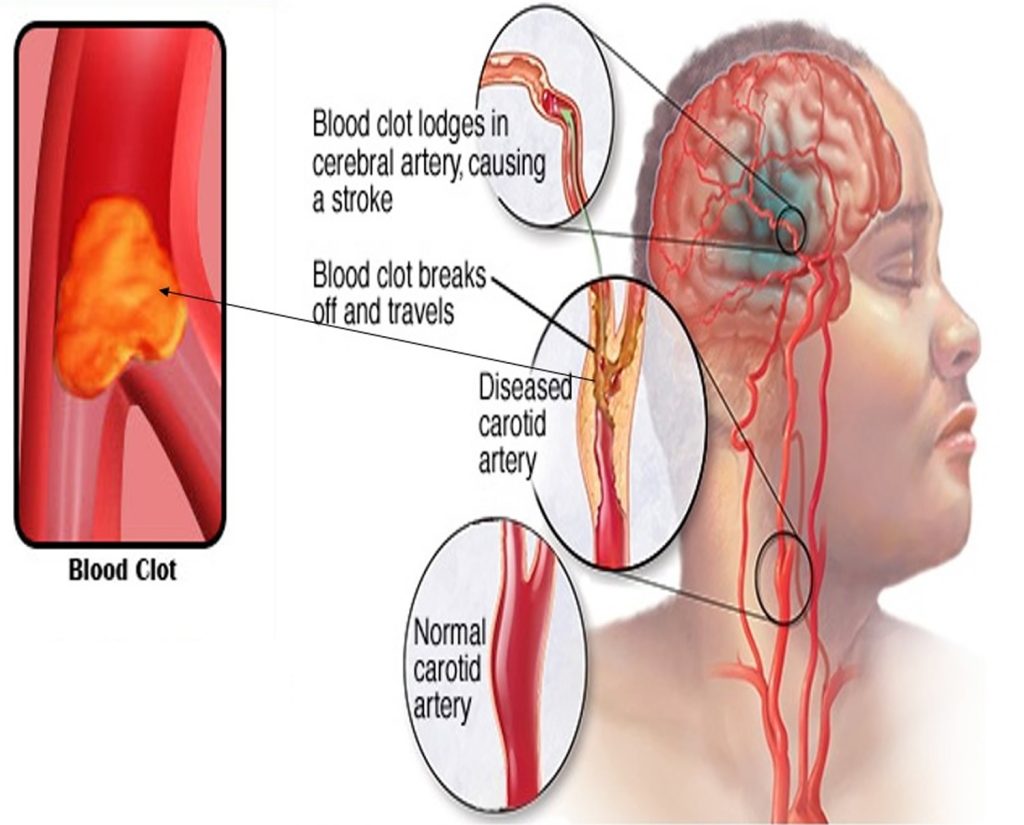
A hemorrhagic stroke, also known as a cerebral haemorrhage, occurs when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures, causing bleeding in the surrounding tissue. This type of stroke is less common than ischaemic stroke, accounting for approximately 13% of all strokes. However, it is more severe and has a higher mortality rate. In this article, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of hemorrhagic stroke.
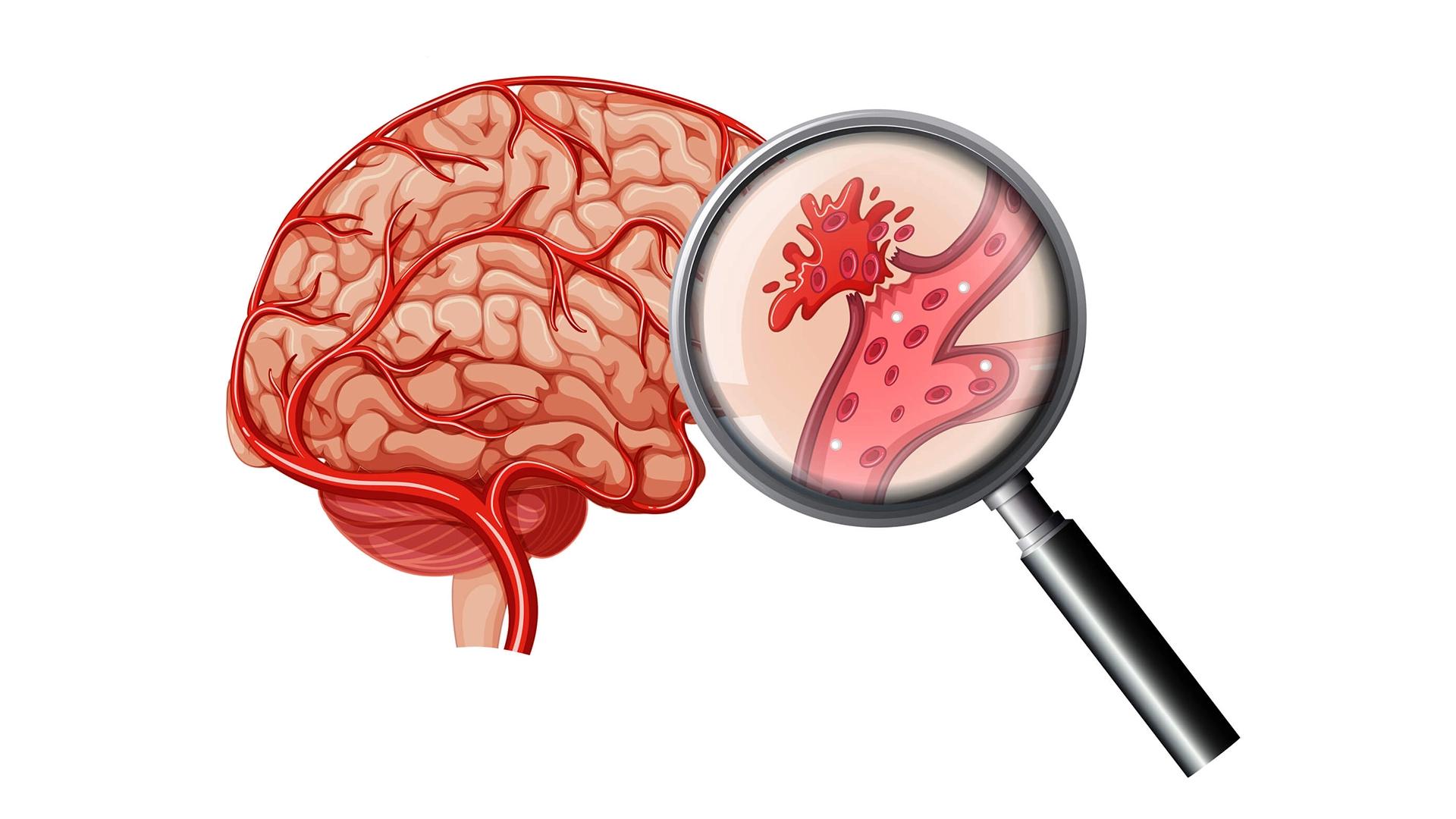
Causes of Hemorrhagic Stroke
Hemorrhagic stroke is caused by the rupture of a blood vessel in the brain, which can be due to various factors, including:
1. Hypertension: High blood pressure can cause blood vessels to weaken and rupture.
2. Aneurysms: Aneurysms are weak spots in blood vessels that can rupture and cause bleeding.
3. Arteriovenous Malformations (AVMs): AVMs are abnormal connections between blood vessels that can rupture and cause bleeding.
4. Blood Clots: Blood clots can form in blood vessels and rupture, causing bleeding.
5. Trauma: Head trauma can cause blood vessels to rupture and bleed.
6. Tumours: Tumours can cause blood vessels to rupture and bleed.
7. Amyloid Angiopathy: Amyloid angiopathy is a condition in which abnormal proteins accumulate in blood vessels, causing them to weaken and rupture.
Symptoms of Hemorrhagic Stroke
The symptoms of hemorrhagic stroke can vary depending on the location and severity of the bleeding. Some common symptoms include:
1. Sudden Severe Headache: A severe headache that comes on suddenly, often described as the worst headache of one’s life.
2. Confusion and Disorientation: Confusion, disorientation, and difficulty speaking or understanding speech.
3. Weakness or Numbness: Weakness or numbness in the face, arm, or leg on one side of the body.
4. Vision Changes: Blurred vision or loss of vision in one eye.
5. Seizures: Seizures can occur due to the bleeding in the brain.
6. Loss of Consciousness: Loss of consciousness or coma can occur due to the severity of the bleeding.
Diagnosis of Hemorrhagic Stroke
Diagnosing hemorrhagic stroke typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests. Some common diagnostic tests include:
1. Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: A CT scan uses X-rays to create detailed images of the brain.
2. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): An MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the brain.
3. Angiography: Angiography uses X-rays and a contrast agent to create detailed images of the blood vessels in the brain.
4. Lumbar Puncture (LP): An LP involves removing a sample of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the spinal canal to check for bleeding.
Treatment of Hemorrhagic Stroke
Treatment for hemorrhagic stroke typically involves a combination of medications and medical procedures. Some common treatments include:
1. Surgery: Surgery may be necessary to relieve pressure on the brain, repair damaged blood vessels, or remove the blood clot.
2. Medications: Medications such as blood pressure medications, anti-seizure medications, and pain medications may be prescribed to manage symptoms and prevent further bleeding.
3. Rehabilitation: Rehabilitation therapy, such as physical, occupational, and speech therapy, may be necessary to help the individual regain lost functions and abilities.
Prevention of Hemorrhagic Stroke
Preventing hemorrhagic stroke requires managing risk factors and making lifestyle changes. Some common prevention strategies include:
1. Blood Pressure Control: Managing high blood pressure through lifestyle changes and medication.
2. Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking to reduce the risk of hemorrhagic stroke.
3. Exercise Regularly: Regular physical activity can help lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
4. Healthy Diet: Eating a healthy diet that is low in salt, sugar, and unhealthy fats can help lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
5. Stress Management: Managing stress through techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises can help lower blood pressure.
Conclusion
Hemorrhagic stroke is a life-threatening condition that requires prompt medical attention. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of hemorrhagic stroke, individuals can take steps to reduce their risk and improve their overall health. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of hemorrhagic stroke, call emergency services immediately.