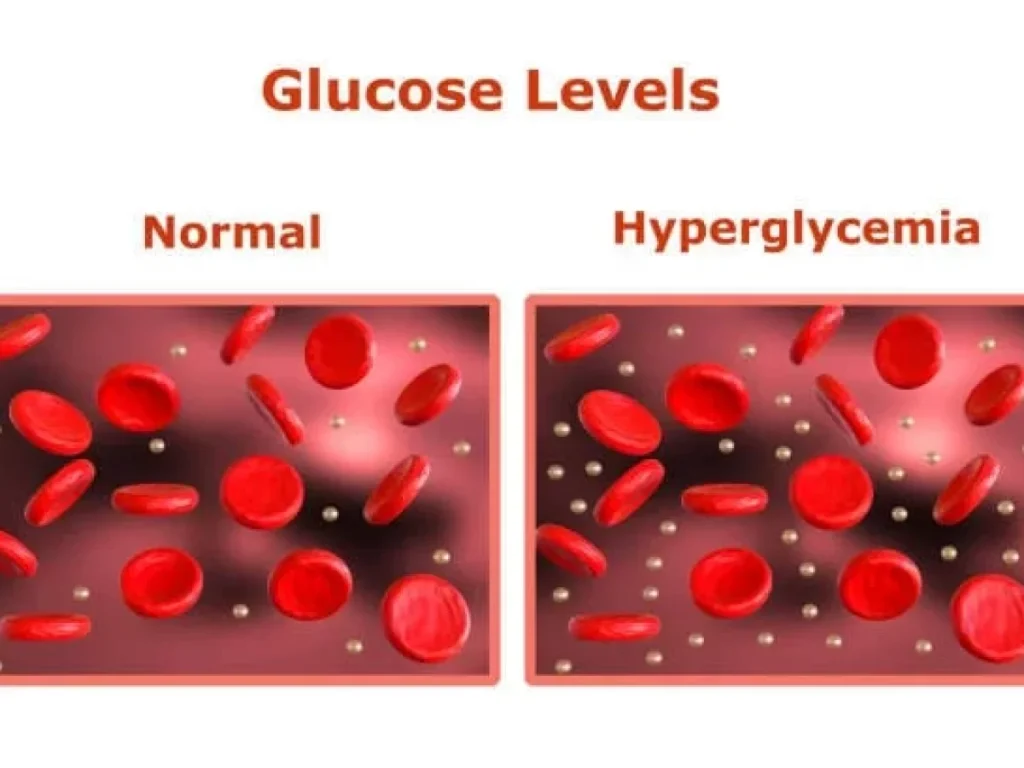
Diabetes is a chronic medical condition characterized by high blood sugar levels. It affects millions worldwide, causing significant health complications if left unmanaged. This article provides an overview of diabetes, its types, symptoms, complications, and management strategies.
Types of Diabetes
1. Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune disease where the pancreas produces little to no insulin.
2. Type 2 Diabetes: The body becomes resistant to insulin, leading to high blood sugar.
3. Gestational Diabetes: Developed during pregnancy due to hormonal changes.
4. LADA (Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults): A form of type 1 diabetes developing in adulthood.
5. MODY (Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young): A rare genetic form of diabetes.
Symptoms
1. Increased thirst and urination
2. Fatigue
3. Blurred vision
4. Slow healing wounds
5. Tingling hands and feet
Complications
1. Heart disease and stroke
2. Kidney disease
3. Neuropathy
4. Retinopathy
5. Foot ulcers and amputation
Management
1. Medication: Oral medications or insulin therapy
2. Diet: Balanced carbohydrate intake and healthy eating
3. Exercise: Regular physical activity
4. Monitoring: Blood glucose tracking
5. Weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight
Lifestyle Changes
1. Healthy eating habits
2. Regular exercise routine
3. Stress management
4. Quit smoking
5. Limit alcohol consumption
Medical Advances
1. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM)
2. Insulin pumps
3. Artificial pancreas
4. Stem cell research
5. Personalized medicine
Conclusion
Diabetes requires careful management to prevent complications. Understanding its types, symptoms, and management strategies empowers individuals to take control of their condition.
References:
American Diabetes Association
World Health Organization
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases